Ultimate Web3 guide for Crypto Curious
Hands-on guides and resources for Web3 builders, investors & learners
Whether you are an operator, builder, investor or just crypto curious - you need to wrap your head around the endless list of resources and information available across the internet. We made it simple and put together a framework that will help you navigate the complex ecosystem of constantly evolving information in the Web3 world. You can build a theoretical knowledge of Web3 stack from different perspectives (as a beginner or blockchain developer) or get hands on experience on these concepts. These resources are meant to help aspiring Web3 Product Managers, investors and blockchain developers (and basically anyone who set their heart to learn more about Crypto) to also get a quick hands-on experience on various basic topics such as non custodial wallets, transacting on different blockchains like Ethereum & Polygon, trading or swapping crypto coins like ETH, DAI & MATIC , buying different NFTs like ERC721 & ERC1155 on OpenSea, transacting on centralized & decentralized exchanges, etc.
Here is the summary of the 3 sections for this Web3 guide from Cryptechie:
Web 3 stack: Overview of Web3 stack and what you need to know
Resources, guides and best articles: A list of constantly updating notion pages and databases full of crypto and web3 resources
Learning by doing exercises: Quick hands-on experience on various basic topics such as non custodial wallets like metamask & coinbase wallet, transacting on different blockchains like Ethereum & Polygon, trading or swapping crypto coins like ETH, DAI & MATIC , buying different NFTs like ERC721 & ERC1155 on OpenSea, transacting on centralised & decentralised exchanges, etc
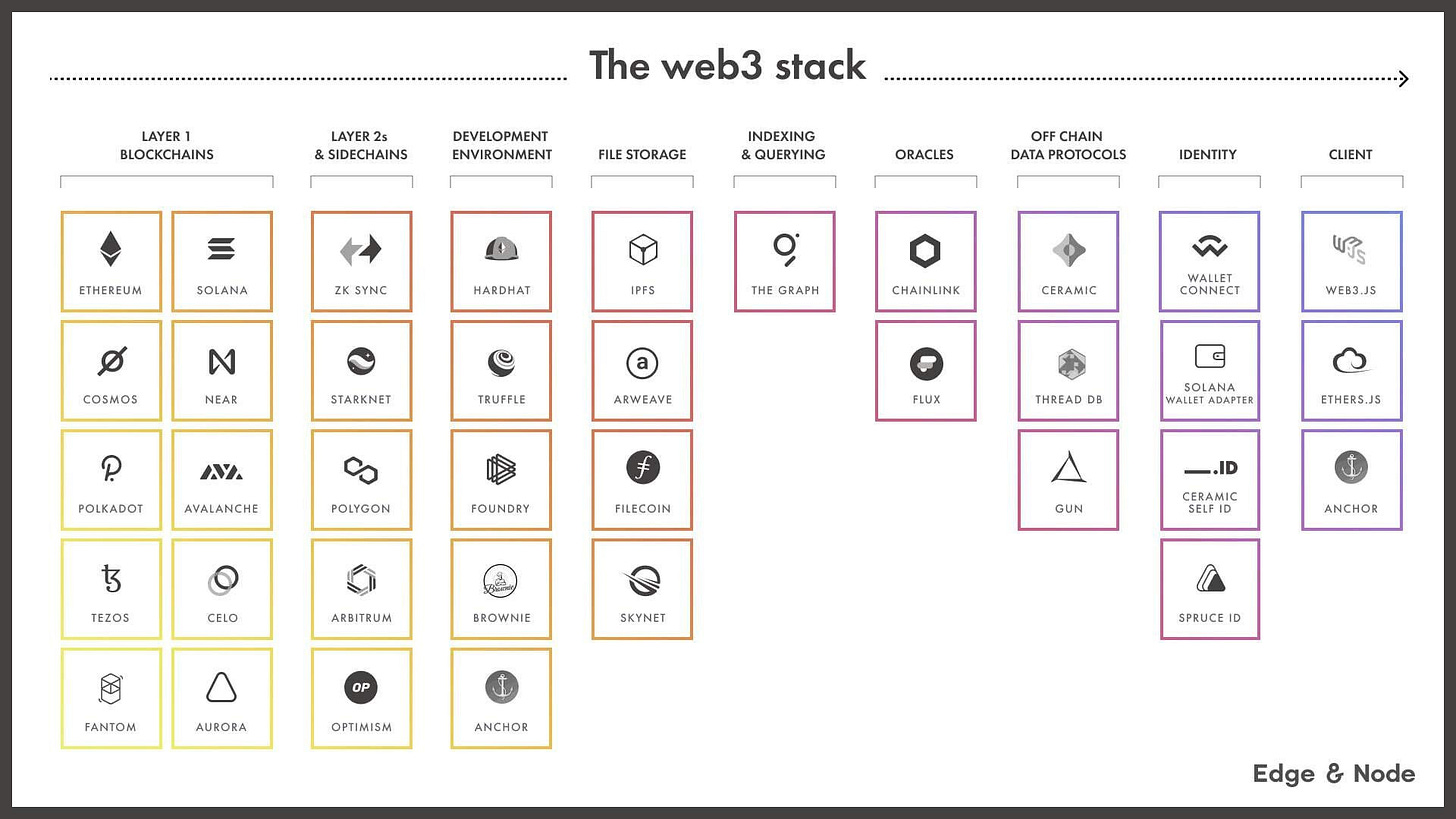
1. Web 3 stack
The Crypto ecosystem can be better unpacked as a six-layer cake model¹, ranging from the basic settlement/mining layer, all the way through the consumer-facing decentralized application and access layer. Between the consumer facing access layer and mining is a spectrum of infrastructure providers, hybrid infrastructure application tools known as primitives, and composable applications that codify, enable and make accessible the various use cases across the crypto ecosystem.
A. If you are a beginner and want to understand Web 3 stack at a high level
A guide to Web3 and Blockchain stack by @Suhail
Blockchains
The base of Web3 stack is the blockchains network. These are divided into 2 types. The first layer refers to the base level of blockchain(its main structure) such as Ethereum and BNB. However layer 2 refers to networks built on top of layer 1 blockchains.
Authentication
These are the tools/wallets that is used to authenticate a user inside of applications. Metamask and Wallet connect are the most popular wallets.
Languages
In order to write smart contracts we need a programming Language. Popular ones are Solidity, Vyper and Rust. Each one has their own pros and cons.
SDKs
Building functionalities from scratch can be a little time-consuming, therefore we can use Web3 SDKs to make the development process much faster. thirdweb, Moralis are great examples.
Frontend Development
To develop the UI for Web3 application you would need a framework such as React, Angular or Vue. Developer can use any of them however for react there are many resources available online.
Oracles
Blockchain oracles are tools that connect blockchains to external systems. They act as a bridge between blockchains and off chains. Chainlink is the most popular price oracle.
Development Environment
This is the place that you write code. When it comes to writing smart contracts, you can either use Remix IDE a local development environment
Web3 Libraries
These are used to interact with the blockchain from client. There are many libraries that does that but the most popular are Ethers.js, Web3.js, and Web3.
Node Providers
Node provider offers a way to access information on blockchain without having your own local blockchain setup. Some of the fastest node providers are Chainstack, Infura and Alchemy.
B. If you are an engineer / Web 3 developer
Defining the web3 stack²
When building a traditional web or mobile application, developers depend on a handful of building blocks to get the job done.
API / app servers (REST or GraphQL)
Authentication layer (managed or hand-rolled)
Database
Client-side frameworks, platforms, and libraries
File storage
So what did this look like in web3?
Blockchain
Blockchain development environment
File storage
Off chain data protocols
API (indexing & querying)
Identity
Client (frameworks and libraries)
Oracles
Other protocols
You can build a full stack web3 app with Next.js, Polygon, Solidity, The Graph, IPFS, and Hardhat
Blockchain - Polygon (with optional RPC provider)
Ethereum development environment - Hardhat
Ethereum web client library - Ethers.js
File storage - IPFS
Indexing and querying - The Graph Protocol
Web3 Application Architecture
Preethi Kasireddy, who worked for a16z over 2013-15 and was an engineer at Coinbase from 2016-17, recently published a blog post that explains the “architecture of Web 3.0 applications.” Backend programming for a dapp is entirely different than for a traditional web application. In Web3, she writes, “you can write smart contracts that define the logic of your applications and deploy them onto the decentralized state machine [i.e. the Ethereum blockchain].” Web servers and traditional databases, in this paradigm, are no longer needed — since everything is done on, or around, the blockchain.
She notes a bit later in the post that “Smart contracts are written in high-level languages, such as Solidity or Vyper.” Solidity was partly inspired by ECMAScript syntax, so it has some similarities to JavaScript (but is very different in other ways).
As for the frontend, that “pretty much stays the same, with some exceptions,”She lays out the simplified Web 3 application architecture in this diagram:
C.If you are growth PM/developer in Web 3, understanding the Web3 Growth Playbook is key³
Web3 Growth Strategies
Partnerships & Integrations
Software companies growing through large BD deals is nothing new and many Web3 projects have adopted this strategy. For example, ChainLink executed on a strategy of closing partnerships during the 2018-2019 bear market and $LINK outperformed as a result.
However, business development can look very different in Web3 when these partnerships are negotiated transparently in governance forums rather than behind boardroom doors. Given that these integrations often do not require permission from one of the two parties, they are not always mutually beneficial. For example, a number of platforms have integrated Curve in ways that do not necessarily benefit Curve itself.
A few examples of Web3 partnership categories:
Token utility - projects that have a native token want to make it as useful as possible. This could include exchange listings, collateral listings (eg adding $LINK to Compound), or a partnership with a DEX to drive additional liquidity.
Distribution - all users interact with DeFi protocols through wallets (Metamask, Rainbow) and increasingly aggregators (Zapper, Zerion). These frontend interfaces control which protocols they show to users and so getting your yield aggregator integrated with wallets can be a big deal.
Lego building - leveraging another DeFi primitive to bring additional utility to your product. For example, Notional leverages Compound to increase its effective yield.
Mergers - the recognition of two teams building in similar directions and no longer making sense to compete has led to protocol mergers, notable Keep & NuCypher and Fei & Rari.
We're starting to see times prioritize hiring a partnerships/BD lead given its increased importance .
Liquidity Mining & Tokenomics
Growth hacking has become incredibly popular over the past decade as marketing has become more analytical and engineering driven. While growth hacking in Web2 has historically been on building affordable, repeatable growth loops, the focus in crypto has been on leveraging a project's native token to drive growth loops.
Liquidity mining is a "a network participation strategy in which a user provides capital to a protocol in return for that protocol’s native token." Just as VC funds helped subsidize marketplaces until they reached scale, Web3 protocols can bootstrap their growth using their native token.
Crypto projects that have grown through token incentives have faced similar challenges to Web2 startups that burned through piles of venture funding. The data is quite clear that most subsidized liquidity is highly mercenary. Hence, we're starting to see more thought out liquidity mining products including OHM and Rift.
Community
If Web2 companies have focused on driving loyalty amongst their uses in the form of engagement and retention, Web3 companies are focused on driving user ownership. One of the most exciting and unique features of Web3 is that "users...fund the products, information, and services that they consume." We're still very early in understanding all of the downstream implications of this innovation.
We think community is critical in a network growth context because engaged communities will give networks leverage in everything they do. This is evident if you look at the Twitter feeds of projects with engaged communities - every announcement sees a ton of engagement and retweets.
Communities can substitute or complement key stakeholders in Web3 projects:
Early customers (and cheerleaders) - having a small group of fanatical customers is crucial for any startup. Community members can serve this role (and then some) because they're both early customers and have meaningful upside
Leverage core team - community members can help with hiring, token design, fundraising (things investors historically helped with)
Extend core team - community members can provide both technical and non-technical support to the core team. Sometimes they step up and join core team, other times this happens more ad-hoc.
Distribution - upstart token projects want to partner with other projects with large communities, just like new products look for distribution in channels with a large footprint
D. If you just want to know more about real world use cases for Web 3
To grasp the power of Web3 , imagine the following ideas of how web3 could improve or disrupt the most successful companies⁴:
Amazon logistics
Instead of having large distribution centers, Use decentralized mini warehouses (e.g. your backyard) for storage & drivers pick up merchandises from closest storage location. Delivery fees paid in warehouse tokens are earned by warehouse owners.
Meta / Facebook
Users earn the platform token by posting and commenting. Amount earned is based on popularity of content posted. Advertisers pay for ads in the platform token.
Google
If the search engine / browser records any user data—e.g. demographic, behavioral— into its database, user earns the platform token. Advertisers pay in platform token to access the database.
Costco
Customers purchase store membership in NFT. They can rent out the NFT on secondary market to others who want access to Costco discounts but don’t shop frequently. Members get rental incomes. Costco gets more customers.
Pepsi
Pepsi owns dozens of food & beverage brands & regularly acquire new ones. A PepsiCo utility token— which customers can earn when buying from one brand & spend on another brand— could help Pepsi grow new brands by leveraging customers from existing brands it owns.
Comcast / Xfinity
Comcast operates a public WiFi network, which consist of hotspots in public locations, businesses & home gateways. A utility token supported by network revenue, which users can earn when providing hotspot service would improve WiFi coverage & user loyalty.
Netflix
Airdrop Netflix tokens to users-> Let users “stake” tokens on pilot shows they like-> Users earn partial streaming revenue from those shows. Now users have more incentive to help promote their favorite shows which attract more subscribers.
Mercado Libre
Use tokenization to drive traffic & give marketplace vendors more incentive. Vendors earn tokens when the customers they attract to platform make purchases. Vendors can then give the tokens to customers as discount or use tokens to pay for platform commissions.
Airbnb
Hosts & guests earn Airbnb tokens when they receive good reviews. They can use tokens to pay for future booking fees, or lower commission charges, or sell tokens on secondary market to monetize their rewards of being good participants on the platform.
Nike
NFTs matched one-to-one w/ limited-edition shoes maintain rarity even after physical shoes are worn out & gone. A collection of rare sneaker NFTs becomes a store of value, which gives more incentive for customers to buy rare sneakers & allows higher price premium.
Starbucks - they already announced it!
A visual exploration of the REAL use cases of NFTs by @Shivsak
Resources
A list of constantly updating notion pages and databases full of crypto and web3 resources
Gaby's Web3 Reading List (One of the best resources!)
The Library by @CuriousAddys: Consider this your community portal to a world of web3 knowledge!
Token Economics Resource List: This is an open source list of valuable tokenomics resources
Working in web3 handbook by @smsunarto
Monday DeFi Market Alpha: Weekly DeFi news summarized
A long list of 1600+ blockchain/crypto/Web3 projects with 1-liner description
List of 24 top resources to get up to speed quickly
Evergreen articles & research on Web 3
Best books on Ethereum (Mastering Ethereum) and Bitcoin (Mastering Bitcoin)
Crypto/Web3 Startup Ideas by DeFi alliance
How web3 is shaping the future of finance by 11FS
FT report on Blockchain - A basic blockchain industry report
The Complete Guide to Full Stack Ethereum Development
Building Full Stack dApps with React, Ethers.js, Solidity, and Hardhat
Guide to L2 / roll-ups by Vitalik and L2 comparision by The Block
What I'm frustrated by in crypto - an honest piece
Transition to web3: a guide for non-technical roles
👩🏫 1. Start with basics (how & why)
Start here to learn the fundamentals of blockchain and crypto.
✍️ 2. Consume & create content
Curated information sources so you can stay up to date on web3.
Jump in and use decentralized applications to gain more familiarity with web3.
Double down on sub-sectors within web3 that you’re passionate about.
Join a DAO to build out your network and start contributing to various communities.
Find a full-time role or part-time earnings opportunities in web3.
3. Learning by doing
Quick hands-on experience on various basic topics such as non custodial wallets like metamask & coinbase wallet, transacting on different blockchains like Ethereum & Polygon, trading or swapping crypto coins like ETH, DAI & MATIC , buying different NFTs like ERC721 & ERC1155 on OpenSea, transacting on centralised & decentralised exchanges, etc Learning by doing in partnership with Tony Mathew1
Buying crypto currencies in a centralised exchange
Experimenting with DeFi and DApps : Aave on Polygon Chain
Swapping coins on a Decentralised Exchange (DEX)
Buying an NFT on OpenSea marketplace
Importing NFTs to non custodial wallet like Metamask
Multiple non custodial or self custodial wallets using the same seed phrase or recovery phrase
Transferring between Ethereum and Polygon blockchains
Experimenting with wallets for other blockchains : Phantom wallet for Solana blockchain
Buying crypto currencies in a centralised exchange
A centralised exchange like Binance or Coinbase is similar to traditional stock exchanges in the sense that they allow to have an account with a simple login instead of dealing with private key or seed phrase. They abstract and handle these details for you. Also they allow you to buy or sell crypto coins using fiat money via different options including credit and debit cards. For this tutorial I am using Binance exchange and INR as currency.
To get started in an exchange or even a wallet, users are typically required to do an online KYC to verify their identity to ensure safety in such platforms. This is the screen that asks for such details. In Binance & earlier in Metamask also the committed time to finish KYC was 2 days, but it got completed in less than 2 hours.
On choosing Indian Rupees (INR) as currency, Binance gives me an option to buy crypto coins via P2P transactions , ie I am directly paying to a seller who wants to sell the particular coin I am looking to buy . Limitation with P2P is that it is a manual process. The exchange will hold the coins in custody from the seller, buyer transfers money to seller directly, then seller has to give confirmation to exchange on recieving funds and then exchange will transfer the coins to the buyer.
In this example I bought around 19 MATIC tokens on Polygon chain using FIAT money which is INR. Now the coins will reflect in trading wallet section of my Binance account. As a next step, I want to move it out of the centralised exchange to my fully controlled ethereum address so that I can manage the coins using my own non custodial wallet in a purely decentralised manner without any centralied exhanged acting as an intermediary. Remember once you have a private key and account(s) for Ethereum , the same is valid for other EVM compatible blockchains like Polygon and Solana and even testnets like Rinkeby and Kovan. So here I am using the address of my account 1 in my metamask wallet for ethereum chain to send the MATIC tokens on Polygon chain.
Since the transaction is happening on Polygon, you can see how low the gas fee is . If I had ETH and was trying to send to the same address on ethereum chain, then the gas fee would have been much higher. It may take upto 10 minutes as shown below for the transacion to be complete and the coins to be visible against your address.
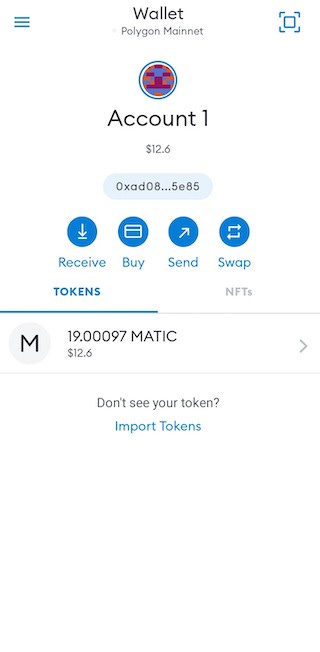
Now in my metamask wallet, on choosing Polygon mainnet as the network, I am able to see the MATIC tokens against my address
Experimenting with DeFi and DApps : Aave on Polygon Chain
Once you have coins on a blockchian, you can also experiment with DApps (Decentralised Applications) especially DeFi (Decentralised Finance) apps . I have used some of the MATIC coins on Polygon that were purchased earlier to get hands on with Aave. As per the polygon blogpost https://blog.polygon.technology/polygons-defi-series-aave/
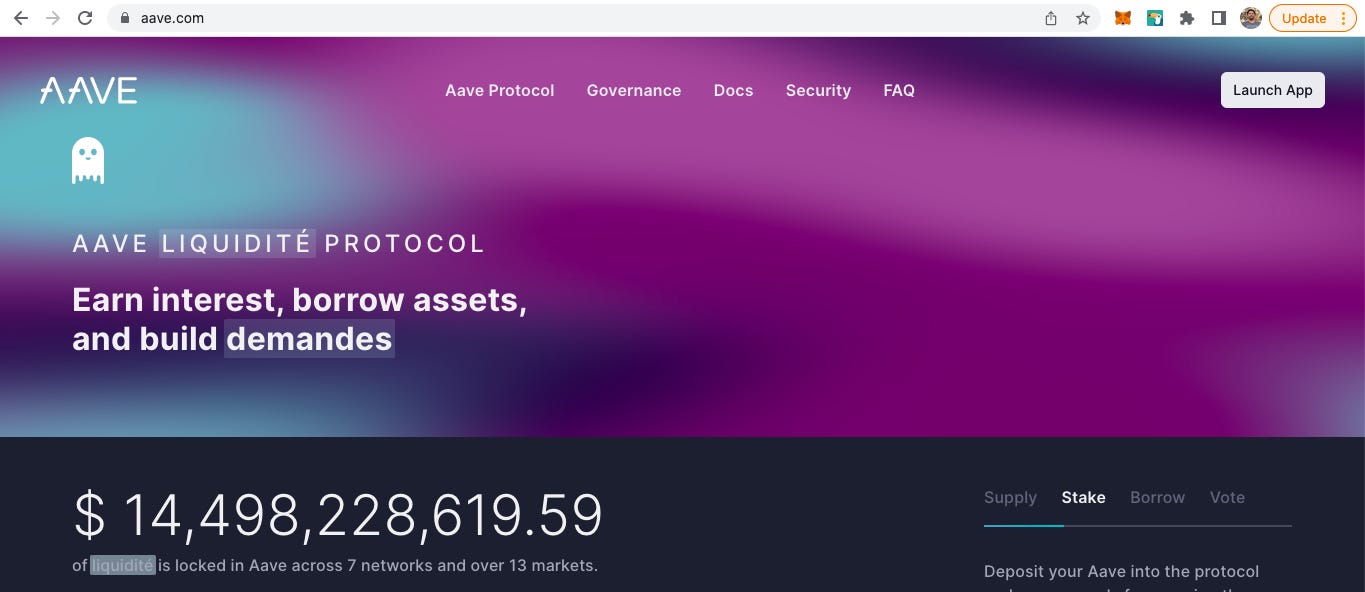
The Aave protocol is an open-source non-custodial decentralised liquidity protocol built on the Ethereum blockchain. It is the largest DeFi protocol in the world (by total value locked) and has a distributed team of over 70 people all over the world. The Aave protocol allows users to supply and borrow cryptoassets and earn yield on cryptoassets supplied to the protocol.
Go to aave.com and connect Launch App and then connect your wallet
When Ethereum mainnet is the chosen network on my metamask wallet, Aaave will show me the coins and the APY I can earn for them and also gives me option to borrow
On clicking supply you can see the the next screen that will show the gas fee. Since I am on ethereum network, the fee will be higher.
Now I switch to polygon network on my wallet and in Aave DApp to see my coins listed with option to Supply
On clicking Supply for MATIC it will show me the gas fee, which is very low on Polygon network as against the Ethereum chain
I went through with the transaction and then after it is complete , I can see that I have supplied 1 MATIC or approx 0.66$ to Aave so that I can start earning interest. I have the option to withdraw the amount or swap for another coin which will provide a different APY
Swapping coins on a Decentralised Exchange (DEX)
DEX or a Decentralised Exchange allows a crypto user to trade on crypto coins by swapping one coin for another. The process is achieved using a concept called Liquidity Pool which exists different pairs of coins. You can easily find detailed writings on the topic in the internet. Below you can see how this can be done on both Polygon and Ethereum chains.
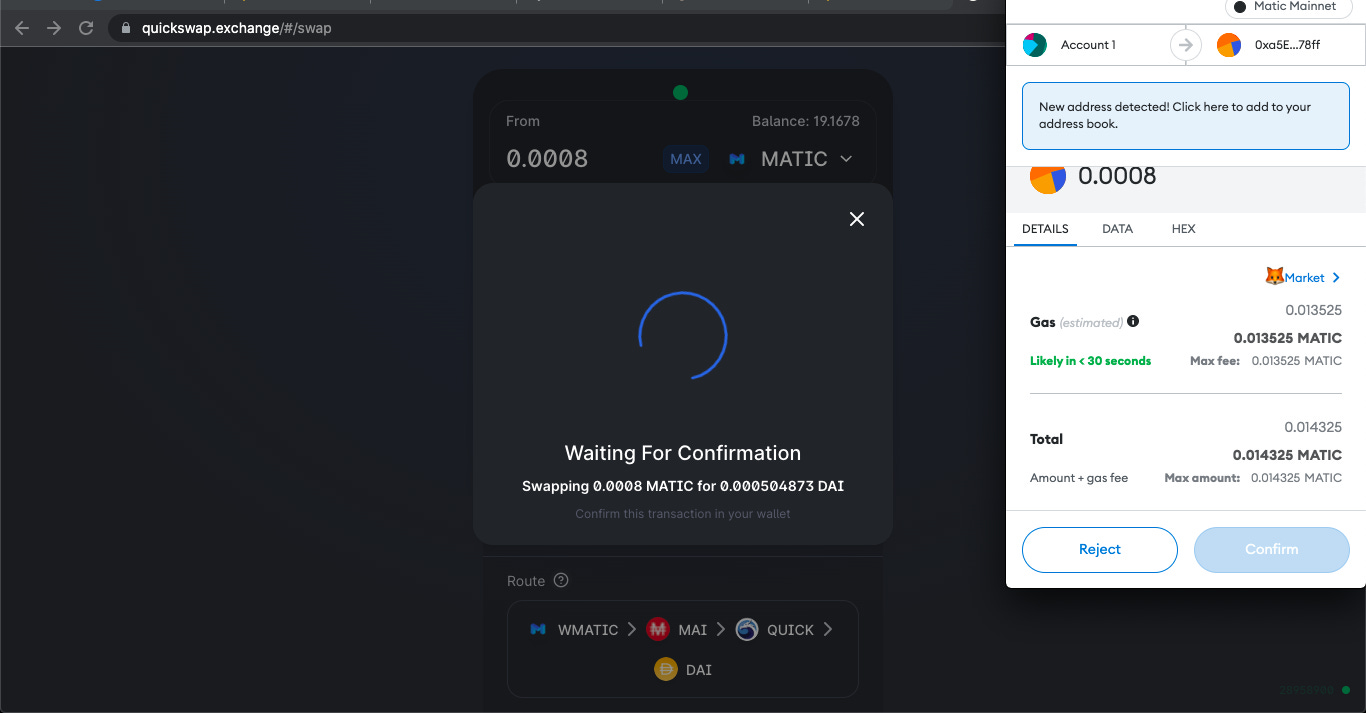
1, QuickSwap on Polygon chain : QuickSwap is a DEX on Polygon chain. In an earlier part I had shown how I bough MATIC on Binance exchange and then sent them to my address. Now I will be swapping some of those MATIC tokens for WETH (Wrapped Ether) and DAI tokens. For example in the screen, I choose to swap some MATIC for DAI and then I need to click confirm
The my metamask wallet will ask me for confirmation and show the gas fee , which is very low and has to be paid in MATIC token , since this entire transaction is on Polygon Chain.
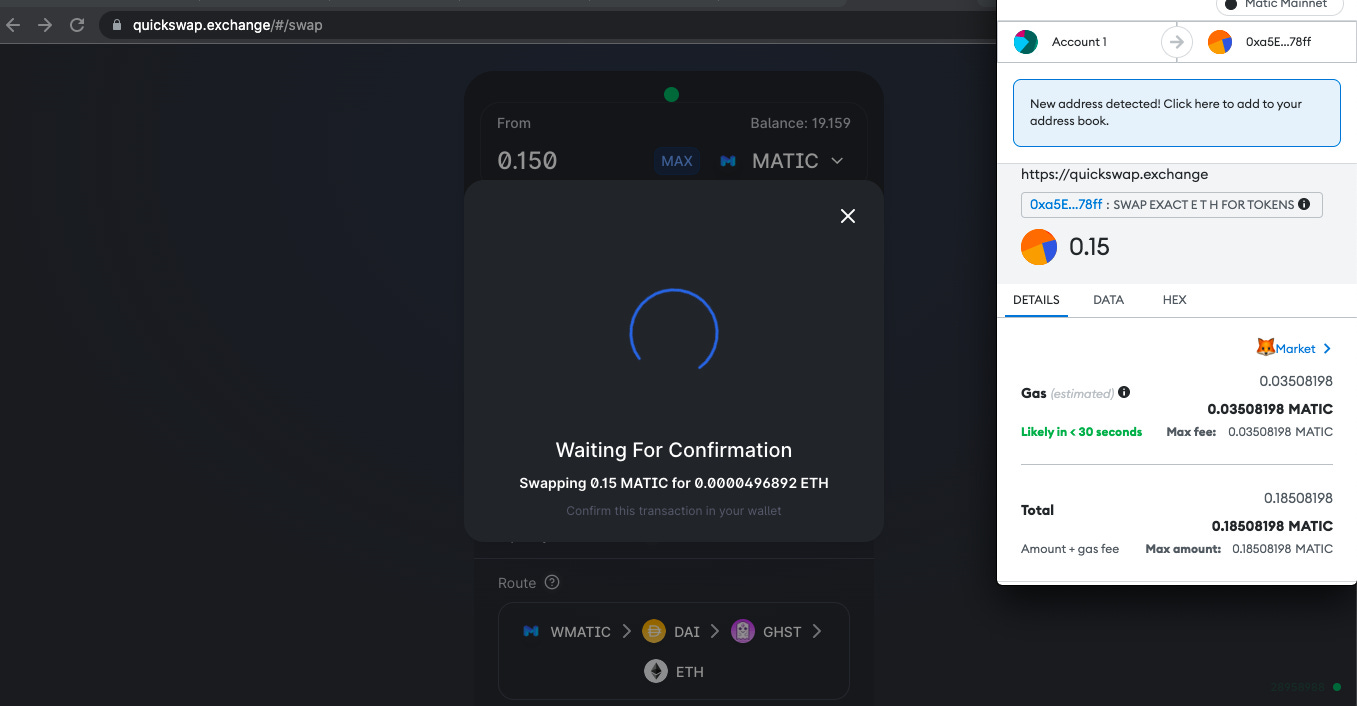
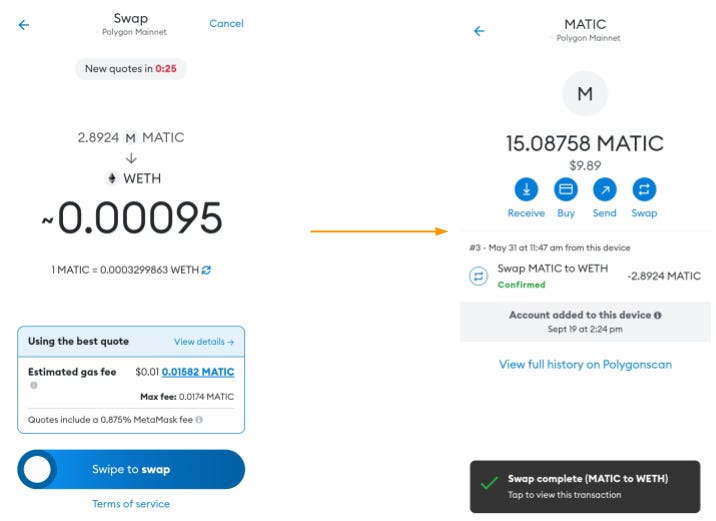
Similarly swapped some MATIC for WETH on Polygon.
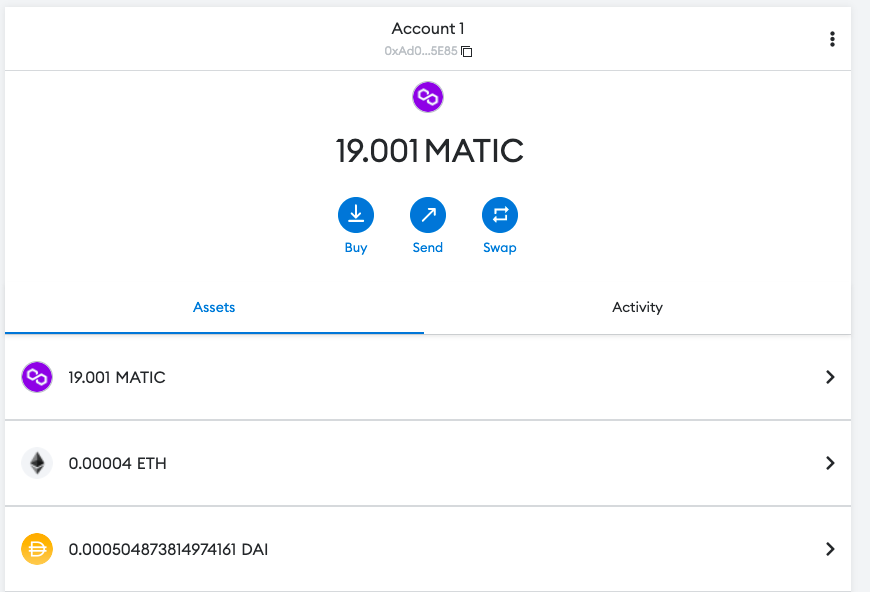
The updated balance of all 3 tokens will show up in the coins dropdown option in QuickSwap and also in metamask web extension
Now, if the tokens are not appearing in metamask wallet, one needs to import the tokens. Click on Import Tokens screen after choosing Polygon Mainnet as the network. For WETH following are the details that can be obtained by seeing the WETH contract page on Poylgon scan. On import, the WETH balance is updated.
Below you can seen how to check in Polygonscan to find the contract address for DAI and then use that to import the tokens in metamask mobile wallet
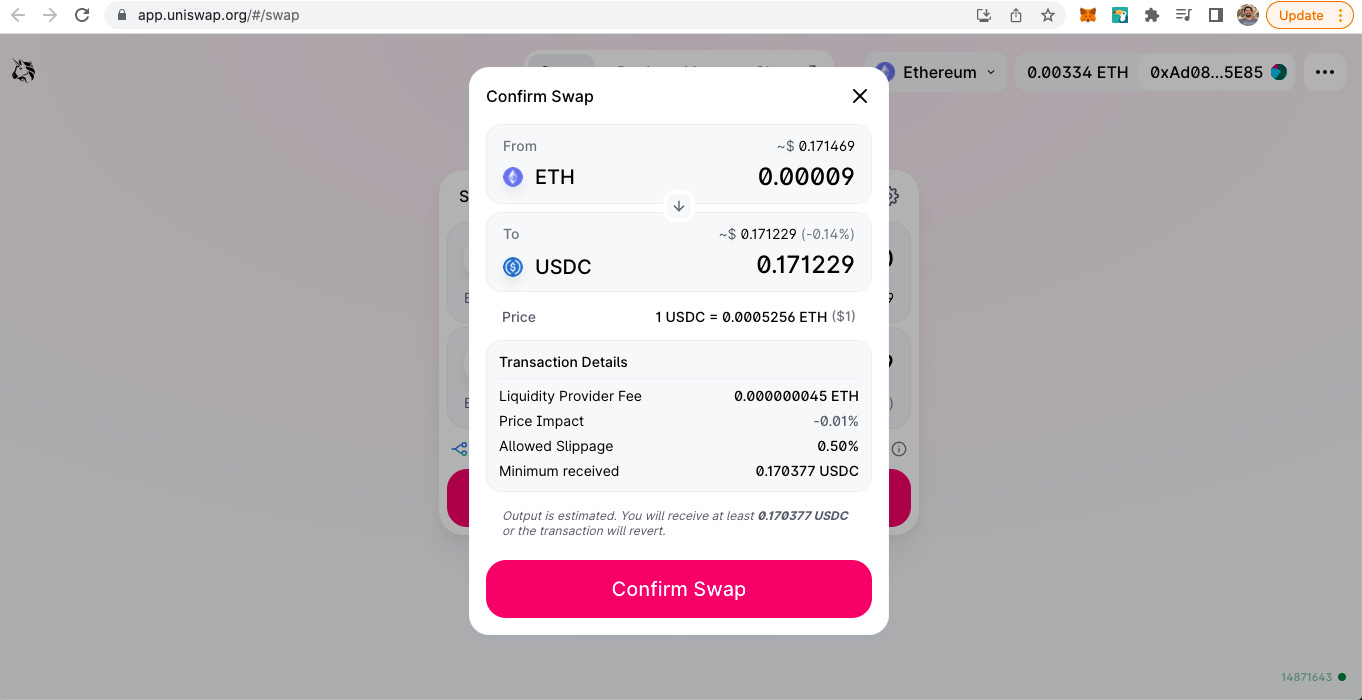
2, UniSwap on Ethereum Chain : UniSwap is a Decentralised Exchange (DEX) on Ethereum blockchain. In the below I am trying to swap some of the ETH in Ethereum chain to get USDC on ethereum chain.
On clicking swap and then on the Confirm Swap on the popup, metamask wallet will popup to show the expected gas fee
In this case I cancelled the transaction after seeing the details as I did not want to execute a transaction with such a high gas fee on ethereum network.
3, Swap within Metamask wallet : Metamask wallet provides a swap option. It is not a standalone DEX like Uniswap or Quickswap, but instead it instead it fetches quotes from multiple DEX aggregrators and suggests user to choose the one with lowest charges.
Here you can see the price quote and gas price estimate for swapping ETH to USDT and WBTC. I did not execute the transactions and cancelled after seeing the price details.
Since gas fee lower in Polygon network , I switched to Polygon mainnet and did a swap of MATIC to WETH at a very low gas fee as shown below
Buying an NFT on OpenSea marketplace
OpenSea is the largest marketplace to buy and sell NFTs. Non-Fungible Tokens can be based on any of the two different standards ERC721 or EC1155. The latter standard actually enables the creations of tokens that are a mix of both fungible and non-fungible. Further, OpenSea allow transactions of NFTs that are based on Ethereum, Polygon or Solana blockchains. In this example below, I am buying a part ownership in an ERC1155 NFT on Polygon. I am doing this so that I can experiment at a very low cost.
1, Add Wrapped Ether for transacting on OpenSea : This is needed because OpenSea allows transactions using WETH which is an ERC20 token. For buying Ethereum NFTs, it must exist on Ethereum chain as WETH on Ethereum and for buying Polygon NFTs, it must exist on Polygon chain as ETH on Polygon .
If there is not enough WETH, more can be added by wrapping ETH balance or MATIC balance based on the chain in which balance is needed . See below example of wrapping ETH to WETH on ethereum
2, Then I searched for Polygon sports NFTs using the search filters and then sorted them by Price: Low to High
3, Checked the details section to confirm it is on Polygon and can also see type as ERC1155
4, To buy the chosen NFT click checkout, complete the Unlock and Sign parts of the transaction by clicking on the wallet , thus completing the purchase.
Importing NFTs to non custodial wallet like Metamask
To view any NFT bought on OpenSea in your metamask wallet , you need to import the NFT with the required details like contract ID and token ID . Go to your wallet and choose the network based on where the NFTs exist . In this example it is Polygon. On the NFTs tab, click import NFT and then enter the contract address and token ID that can be obtained form OpenSea. On completing the import, the NFT will be displayed in your metamask wallet.
Multiple non custodial or self custodial wallets using the same seed phrase or recovery phrase
For a non-custodial wallet , the 12-words seed phrase or recovery phrase is everything. Hence the major warning signs that you keep seeing on “never to lose this phrase” and to “create safe backups” . Ethereum seed phrases are based on BIP39 standard. It is a code generated when you create a new wallet for ethereum blockhain for the first time using a non-custodial wallet. You can play around on this site https://iancoleman.io/bip39 / to get an idea on the link between the 12-words seed phrase or recovery phrase, private key and public key.
This means that a user can reuse the same phrase in a new non custodial wallet to access the exisinting wallet without having to get a new 12-words mnemonic. I have used the seed phrase that I got while setting up my metamask wallet to import the wallet account to coinbase wallet app as shown below. This way I am able to see all my crypto coins that I hold on Ethereuem and Polygon chains in my coinbase wallet app . This is just by using the same recovery phrase or seed phrase that was provided to me when I had set up my metamask wallet.
Viewing transaction and coins holding details of an address using Etherscan and Polygonscan
Etherscan is the website where you can view details of a transactions and addresses in a more easy to read UI/UX.
You can view the details of the transactions against an address and also the tokens owned by that address by visiting Etherscan. Example : https://etherscan.io/address/0xad085736a7a27009dd346ecd1ce51cfab80c5e85 . If a particular address is also linked to an ENS (Ethereum Name Service) .eth domain, then that can also be used instead of the hexadecimal address. Example : https://etherscan.io/address/tonymathew.eth
As mentioned before, a user will have the same private key, public key and addresses in any other EVM compatible chain. So transactions and coin holdings of a given address on thePolygon network can be viewed by visiting PolygonScan and going to the page for that address . ENS name will work only for Ethereum chain and not for Polygon. Example : https://polygonscan.com/address/0xAd085736A7a27009Dd346ECd1cE51CfAb80c5E85
Transferring between Ethereum and Polygon blockchains
To view any NFT bought on OpenSea in your metamask wallet , you need to import the NFT with the required details like contract ID and token ID . Go to your wallet
1, Visit the website https://wallet.polygon.technology/bridge to do such inter chain transfers via the Polygon Bridge and connect your wallet
2, Ethereum to Polygon transfer needs just one transaction and cost gas fee on the Ethereum network
3, Polygon to Ethereum transfer has two stages with one on Polygon chain and other on Ethereum chain and will take upto 3 hours to be completed
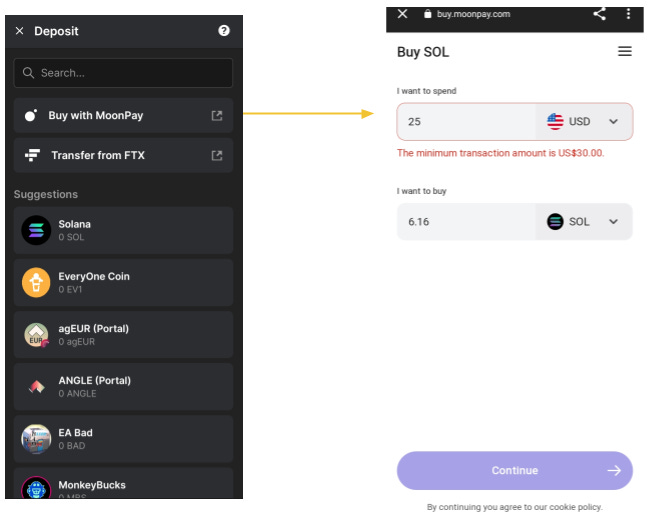
Experimenting with wallets for other blockchains : Phantom wallet for Solana blockchain
Phanton Wallet is a famous wallet for Solana blockchain. If you want you can experiment with it. It provides an option to buy SOL using cards. Since minimum transaction is USD 300, i did not try any transactions. Here are the screens.














































Great resource for anyone entering Web3 world
Amazing guide and resource. I appreciate you putting this together.